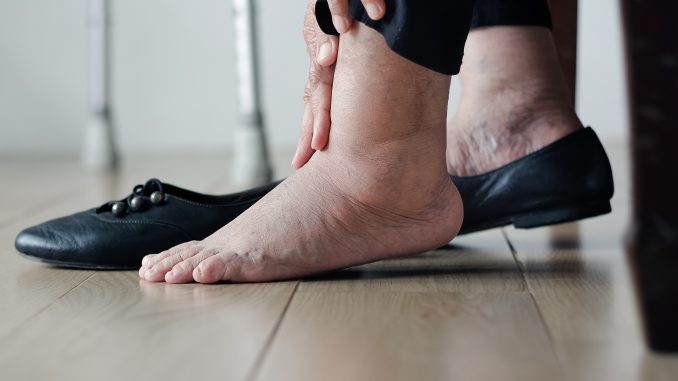
Fluid retention, also known as edema, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body’s tissues. It can lead to swelling in various parts of the body, including the legs, ankles, feet, and hands. While mild fluid retention can be normal, chronic or severe edema may be a sign of an underlying health condition. In this article, we will discuss six common factors that can cause fluid retention and provide tips on how to avoid or manage it.
1. High Sodium Intake:
One of the leading causes of fluid retention is a diet high in sodium (salt). Excessive sodium intake can disrupt the body’s fluid balance, causing it to retain water. Processed and fast foods, canned soups, and restaurant meals are often loaded with sodium. To avoid this:
- Read food labels and choose low-sodium or salt-free options.
- Cook fresh meals at home using herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt.
- Limit your consumption of processed and restaurant foods.
2. Sedentary Lifestyle:
Lack of physical activity can contribute to fluid retention. When you’re inactive, blood circulation may slow down, and fluids may accumulate in the lower extremities. To prevent this:
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Elevate your legs periodically if you have a desk job or spend long hours sitting.
- Stretch and move your legs to promote circulation during extended periods of sitting.
3. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, especially in women, can lead to fluid retention. This often occurs during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause. While you can’t prevent hormonal changes, you can manage their effects:
- Stay hydrated to help your body regulate fluid balance.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Discuss hormonal treatments or birth control options with your healthcare provider if fluid retention becomes a significant issue.
4. Medications:
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and some blood pressure medications, can cause fluid retention as a side effect. If you suspect your medication is causing edema, consult your healthcare provider for potential alternatives or adjustments to your treatment plan.
5. Heart and Kidney Conditions:
Chronic heart and kidney diseases can impair the body’s ability to regulate fluid balance, leading to fluid retention. Managing these underlying conditions is crucial in preventing and managing edema:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing heart and kidney diseases.
- Monitor your blood pressure and follow a heart-healthy diet.
- Limit your intake of alcohol and caffeine, which can exacerbate fluid retention.
6. Excessive Heat:
Hot weather can lead to increased sweating, causing temporary fluid loss. Paradoxically, your body may respond by retaining more water to compensate for the loss. To avoid heat-related fluid retention:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoid excessive heat exposure and take breaks in the shade when outdoors.
- Use fans or air conditioning to keep your living space cool.
Conclusion:
Fluid retention can be uncomfortable and may signal an underlying health issue. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes, you can reduce the risk of edema and manage it effectively. If you experience persistent or severe fluid retention, consult with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Making lifestyle changes, such as reducing sodium intake, staying active, and managing chronic conditions, can significantly improve your overall health and help prevent fluid retention.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)